A review of Three.js on Menards Shelving Kiosk
Three.JWhat?


WebGL

3D within the web browser.
- Grew out of Canvas 3D
- Started by Vladimir Vukićević in 2006
- WebGL spec 1.0 (2009)

WebGL is Hard
“It takes a lot of work to set up that damn little WebGL canvas! Initializing the canvas is pretty easy, but in order to get anything to show you need to create your vertex buffer, fill it, bind it properly, write your shader, compile it, link it, bind it, and then dispatch the draw call. And that's only if you don't care about perspective and nothing moves! If you want anything beyond a simple triangle or quad you also need to create some matricies (something that there's no native library for, BTW!) run through the required maths, bind them to the appropriate shader slots, and then render. Oh, and if you want it to be interactive at all now you're doing input handling too. And by the way, where are your vertices coming from anyway? Anything more complex than a cube is impractical to code by hand, so you need a model format that you can export to and parse...
Tired yet?”
- Brandon Jones, Chrome WebGL Implementor at Google
So, What is Three.js?
Three.JS makes WebGL easier.
Three.JS
- JavaScript Library for creating 3D graphics in browsers
- Released by Ricardo Cabello (mrdoob) in 2010
- Multiple renderers: WebGL, Canvas, SVG, DOM
- MIT License -- No dependencies -- 418kB
Native WebGL Code
function WebGL(CID, FSID, VSID) {
var canvas = document.getElementById(CID);
if (!canvas.getContext("webgl") && !canvas.getContext("experimental-webgl"))
alert("Your Browser Doesn't Support WebGL");
else {
this.GL = (canvas.getContext("webgl")) ? canvas.getContext("webgl") : canvas.getContext("experimental-webgl");
this.GL.clearColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0); // this is the color
this.GL.enable(this.GL.DEPTH_TEST); //Enable Depth Testing
this.GL.depthFunc(this.GL.LEQUAL); //Set Perspective View
this.AspectRatio = canvas.width / canvas.height;
var FShader = document.getElementById(FSID);
var VShader = document.getElementById(VSID);
if (!FShader || !VShader)
alert("Error, Could Not Find Shaders");
else {
//Load and Compile Fragment Shader
var Code = LoadShader(FShader);
FShader = this.GL.createShader(this.GL.FRAGMENT_SHADER);
this.GL.shaderSource(FShader, Code);
this.GL.compileShader(FShader);
//Load and Compile Vertex Shader
Code = LoadShader(VShader);
VShader = this.GL.createShader(this.GL.VERTEX_SHADER);
this.GL.shaderSource(VShader, Code);
this.GL.compileShader(VShader);
//Create The Shader Program
this.ShaderProgram = this.GL.createProgram();
this.GL.attachShader(this.ShaderProgram, FShader);
this.GL.attachShader(this.ShaderProgram, VShader);
this.GL.linkProgram(this.ShaderProgram);
this.GL.useProgram(this.ShaderProgram);
//Link Vertex Position Attribute from Shader
this.VertexPosition = this.GL.getAttribLocation(this.ShaderProgram, "VertexPosition");
this.GL.enableVertexAttribArray(this.VertexPosition);
//Link Texture Coordinate Attribute from Shader
this.VertexTexture = this.GL.getAttribLocation(this.ShaderProgram, "TextureCoord");
this.GL.enableVertexAttribArray(this.VertexTexture);
}
this.Draw = function (Object, Texture) {
var VertexBuffer = this.GL.createBuffer(); //Create a New Buffer
//Bind it as The Current Buffer
this.GL.bindBuffer(this.GL.ARRAY_BUFFER, VertexBuffer);
// Fill it With the Data
this.GL.bufferData(this.GL.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(Object.Vertices), this.GL.STATIC_DRAW);
//Connect Buffer To Shader's attribute
this.GL.vertexAttribPointer(this.VertexPosition, 3, this.GL.FLOAT, false, 0, 0);
//Repeat For The next Two
var TextureBuffer = this.GL.createBuffer();
this.GL.bindBuffer(this.GL.ARRAY_BUFFER, TextureBuffer);
this.GL.bufferData(this.GL.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(Object.Texture), this.GL.STATIC_DRAW);
this.GL.vertexAttribPointer(this.VertexTexture, 2, this.GL.FLOAT, false, 0, 0);
var TriangleBuffer = this.GL.createBuffer();
this.GL.bindBuffer(this.GL.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, TriangleBuffer);
this.GL.bufferData(this.GL.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, new Uint16Array(Object.Triangles), this.GL.STATIC_DRAW);
//Generate The Perspective Matrix
var PerspectiveMatrix = MakePerspective(45, this.AspectRatio, 1, 10000.0);
var TransformMatrix = MakeTransform(Object);
//Set slot 0 as the active Texture
this.GL.activeTexture(this.GL.TEXTURE0);
//Load in the Texture To Memory
this.GL.bindTexture(this.GL.TEXTURE_2D, Texture);
//Update The Texture Sampler in the fragment shader to use slot 0
this.GL.uniform1i(this.GL.getUniformLocation(this.ShaderProgram, "uSampler"), 0);
//Set The Perspective and Transformation Matrices
var pmatrix = this.GL.getUniformLocation(this.ShaderProgram, "PerspectiveMatrix");
this.GL.uniformMatrix4fv(pmatrix, false, new Float32Array(PerspectiveMatrix));
var tmatrix = this.GL.getUniformLocation(this.ShaderProgram, "TransformationMatrix");
this.GL.uniformMatrix4fv(tmatrix, false, new Float32Array(TransformMatrix));
//Draw The Triangles
this.GL.drawElements(this.GL.TRIANGLES, Object.Triangles.length, this.GL.UNSIGNED_SHORT, 0);
};
this.LoadTexture = function (Img) {
//Create a new Texture and Assign it as the active one
var TempTex = this.GL.createTexture();
this.GL.bindTexture(this.GL.TEXTURE_2D, TempTex);
this.GL.pixelStorei(this.GL.UNPACK_FLIP_Y_WEBGL, true);
//Load in The Image
this.GL.texImage2D(this.GL.TEXTURE_2D, 0, this.GL.RGBA, this.GL.RGBA, this.GL.UNSIGNED_BYTE, Img);
//Setup Scaling properties
this.GL.texParameteri(this.GL.TEXTURE_2D, this.GL.TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, this.GL.LINEAR);
this.GL.texParameteri(this.GL.TEXTURE_2D, this.GL.TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, this.GL.LINEAR_MIPMAP_NEAREST);
this.GL.generateMipmap(this.GL.TEXTURE_2D);
//Unbind the texture and return it.
this.GL.bindTexture(this.GL.TEXTURE_2D, null);
return TempTex;
};
}
}
function MakePerspective(FOV, AspectRatio, Closest, Farest) {
var YLimit = Closest * Math.tan(FOV * Math.PI / 360);
var A = -(Farest + Closest) / (Farest - Closest);
var B = -2 * Farest * Closest / (Farest - Closest);
var C = (2 * Closest) / ((YLimit * AspectRatio) * 2);
var D = (2 * Closest) / (YLimit * 2);
return [
C, 0, 0, 0,
0, D, 0, 0,
0, 0, A, -1,
0, 0, B, 0
];
}
function MakeTransform(Object) {
var y = Object.Rotation * (Math.PI / 180.0);
var A = Math.cos(y);
var B = -1 * Math.sin(y);
var C = Math.sin(y);
var D = Math.cos(y);
Object.Rotation += .3;
return [
A, 0, B, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0,
C, 0, D, 0,
0, 0, -6, 1
];
}
function LoadShader(Script) {
var Code = "";
var CurrentChild = Script.firstChild;
while (CurrentChild) {
if (CurrentChild.nodeType == CurrentChild.TEXT_NODE)
Code += CurrentChild.textContent;
CurrentChild = CurrentChild.nextSibling;
}
return Code;
}
var Cube = {
Rotation: 0,
Vertices: [ // X, Y, Z Coordinates
//Front
1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
1.0, -1.0, -1.0, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0, -1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
//Back
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0, 1.0, -1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
//Right
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
//Left
-1.0, 1.0, 1.0, -1.0, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0, -1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
//Top
1.0, 1.0, 1.0, -1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
1.0, -1.0, -1.0, -1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
//Bottom
1.0, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
1.0, -1.0, -1.0, -1.0, -1.0, -1.0
],
Triangles: [ // Also in groups of threes to define the three points of each triangle
//The numbers here are the index numbers in the vertex array
//Front
0, 1, 2,
1, 2, 3,
//Back
4, 5, 6,
5, 6, 7,
//Right
8, 9, 10,
9, 10, 11,
//Left
12, 13, 14,
13, 14, 15,
//Top
16, 17, 18,
17, 18, 19,
//Bottom
20, 21, 22,
21, 22, 23
],
Texture: [ //This array is in groups of two, the x and y coordinates (a.k.a U,V) in the texture
//The numbers go from 0.0 to 1.0, One pair for each vertex
//Front
1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0,
0.0, 0.0,
//Back
0.0, 1.0,
0.0, 0.0,
1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 0.0,
//Right
1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0,
0.0, 0.0,
//Left
0.0, 1.0,
0.0, 0.0,
1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 0.0,
//Top
1.0, 0.0,
1.0, 1.0,
0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0,
//Bottom
0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0,
1.0, 0.0,
1.0, 1.0
]
};
//This will hold our WebGL variable
var GL;
//Our finished texture
var Texture;
//This will hold the textures image
var TextureImage;
function Ready() {
GL = new WebGL("GLCanvas", "FragmentShader", "VertexShader");
TextureImage = new Image();
TextureImage.onload = function () {
Texture = GL.LoadTexture(TextureImage);
setInterval(Update, 33);
};
TextureImage.src = "Dirt.jpg";
}
function Update() {
GL.GL.clear(16384 | 256);
GL.Draw(Cube, Texture);
}294 lines
Same Cube in Three.js
Three.js Code
var camera, scene, renderer, mesh;
init();
animate();
function init() {
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setSize( 720, 480 );
document.body.appendChild( renderer.domElement );
camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 70, 720 / 480, 1, 1000 );
camera.position.z = 400;
scene = new THREE.Scene();
var geometry = new THREE.CubeGeometry( 200, 200, 200 );
var texture = THREE.ImageUtils.loadTexture( 'textures/dirt.jpg' );
var material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( { map: texture } );
mesh = new THREE.Mesh( geometry, material );
scene.add( mesh );
}
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame( animate );
mesh.rotation.y += 0.003;
renderer.render( scene, camera );
}(273 lines less)
Interesting?

Hanson,
we have a problem.

- Prior kiosk experience became outdated
- Did not show the depth of their product offering
- Wanted a multi-platform experience
- Difficult to picture a room in 2D
Other WebGL Libraries
- Babylon.js - Made by Microsoft, friendly with IE11,
game targeted - GLGE - Lightweight, was cool before Three.js
- Scene.js - Specialized towards rendering many
individual objects, no fancy effects
All give you easier ways to use WebGL without all the involvement of writing native WebGL
Why was Three.JS Chosen?
Even though it's new, it's actually quite good.
 wow
much forked
such examples
wow
much forked
such examples
100s of well documented and up-to-date examples
By far the most active WebGL library on GitHub
(14,000 stars, forked over 3000 times)
Early Proofs of Concept

Performance Testing
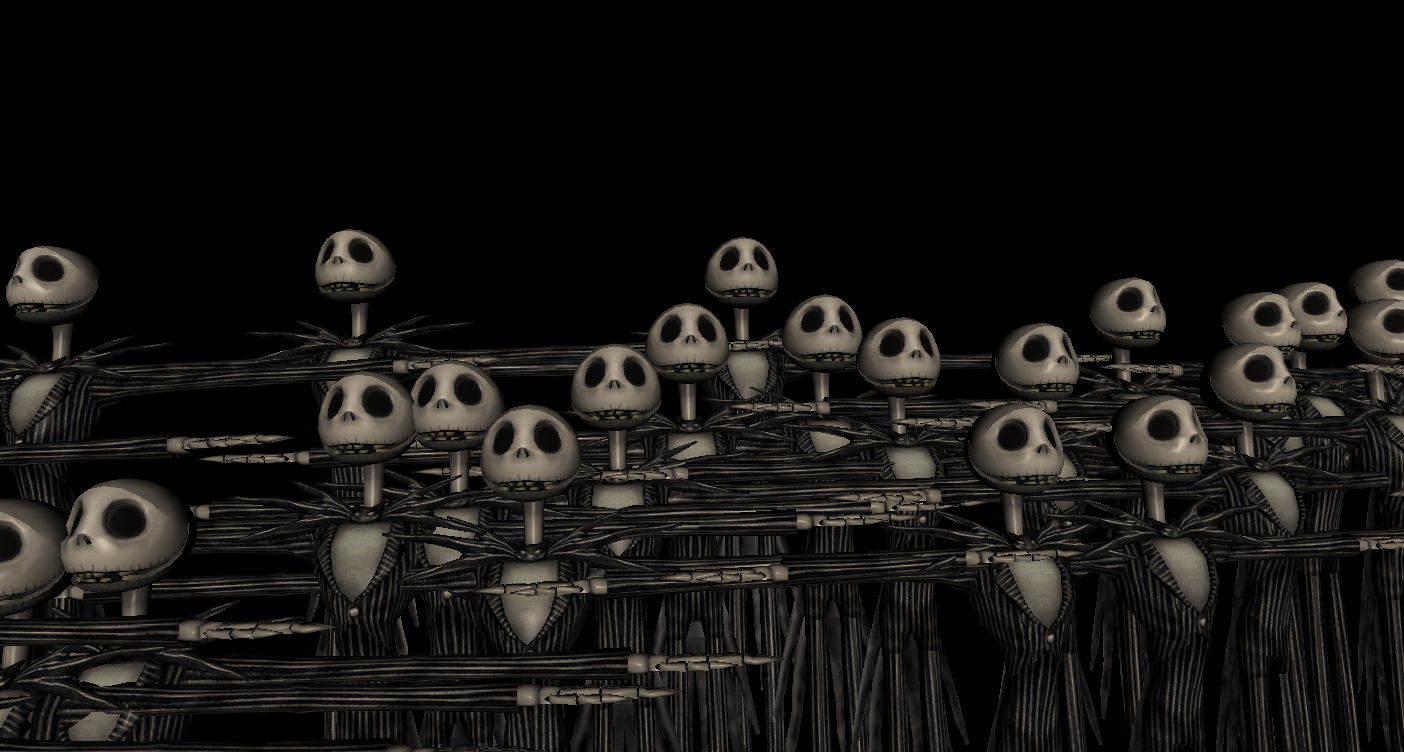

Testing performance with many models and materials
Loading OBJ/MTL files from a 3rd party
Positioning objects in 3D space
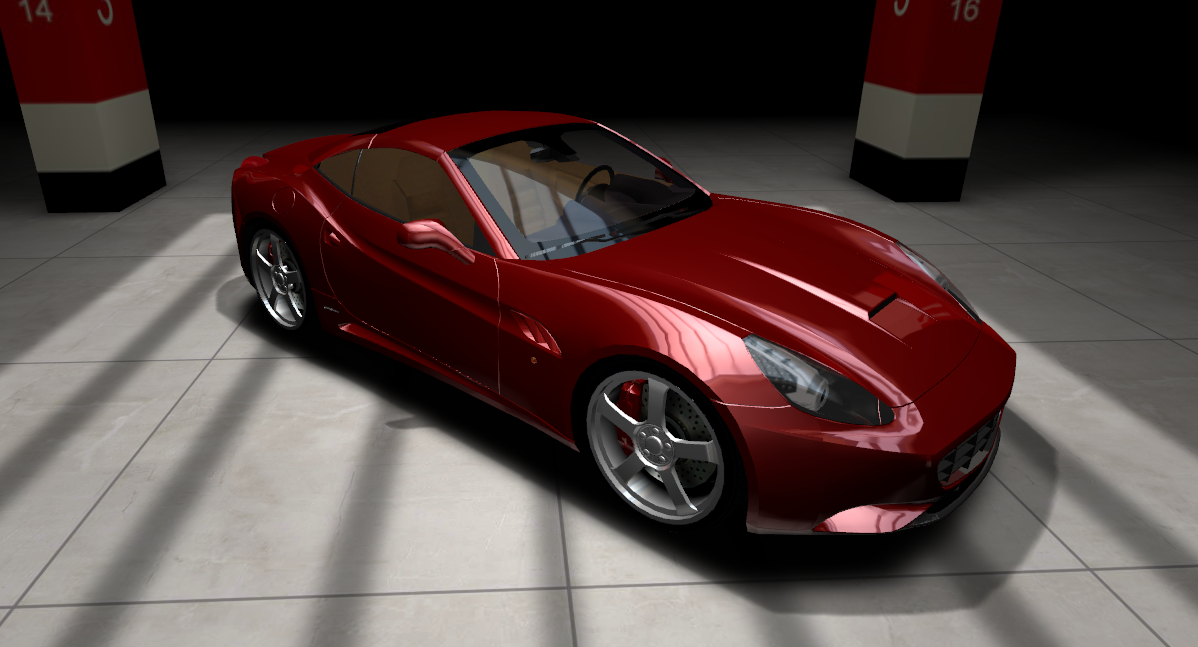
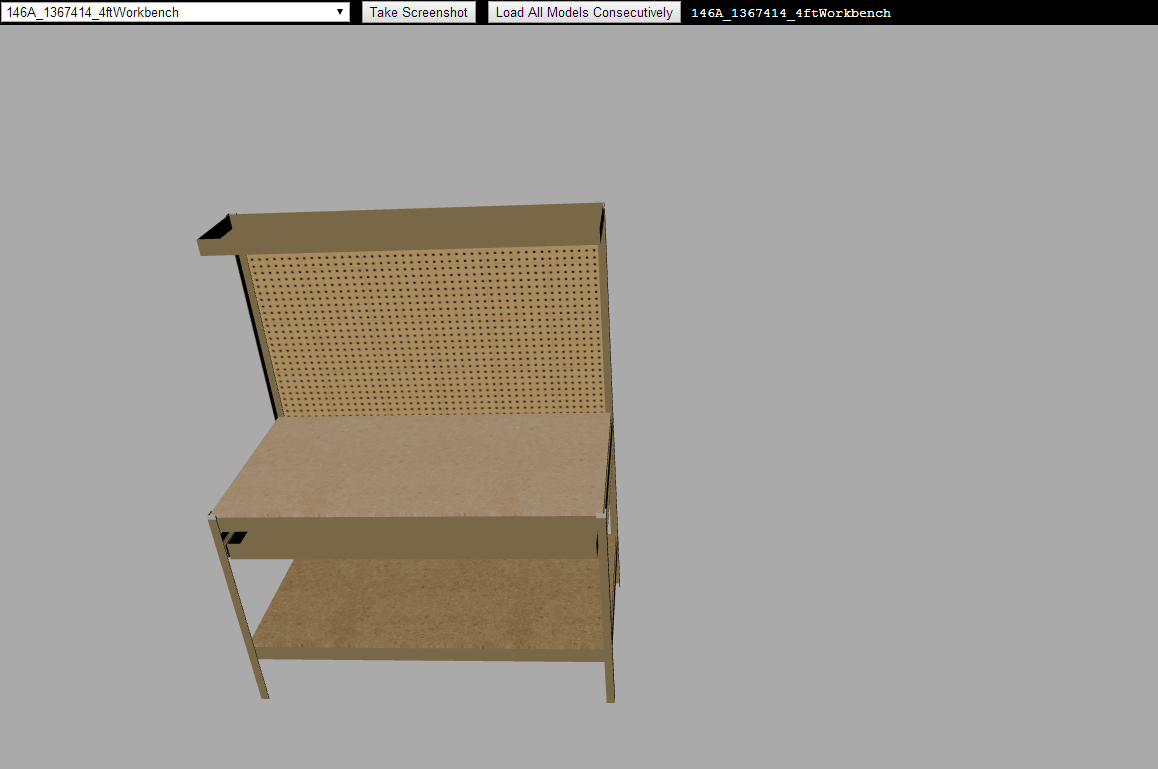
Model Checker
Loads from real models from Menards
Uses the same lighting as the actual kiosk
Allows camera control, model rotation
Checks for errors and tests scaling
Menards Kiosk
Supported model types
Three.js supports many model types, including:
OpenCTM
JSON
OBJ
OBJ/MTL
PLY
Scene files
STL
UTF8 format
VRML
Modeling Tools Used
We're using OBJ/MTL because we had multiple people working on models using different tools. Each tool used could export OBJ/MTL.
Modeling tools used:
- Maya
- Blender
- Cinema 4D
- 3DS Max
- Meshlab
Yes, it has support detection

Detector.js
Comes with Three.js
Checks for browser and graphics card support for WebGL
Displays message in the draw area if no support
3d Models
![]()
File types:
Object file (.obj) - Contains geometry of object
Material file(.mtl) - Contains texture mapping and
lighting information
Image file (.jpg) - Contains bitmap data for texture
2D View
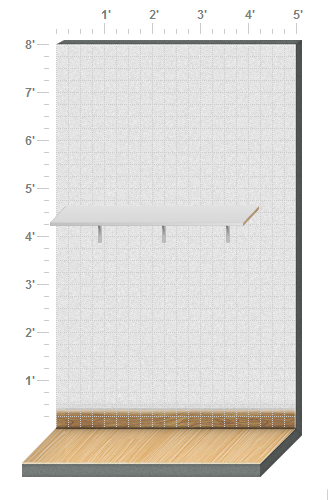
3D View

From Menards Services to Three.js
Menards Server
Menards Web Services
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol)
↳
Hanson Server
↴
WDSL (Web Services Description Language) generated Java Model
↓
Custom Model
↓
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)
↳
Shelving Kiosk (Front End)
↴
Product Side Bar
↓
2D Canvas (configurator)
↓
3D!
Some things we had to keep in mind

Positioning
By default, 3D models are positioned from the center:
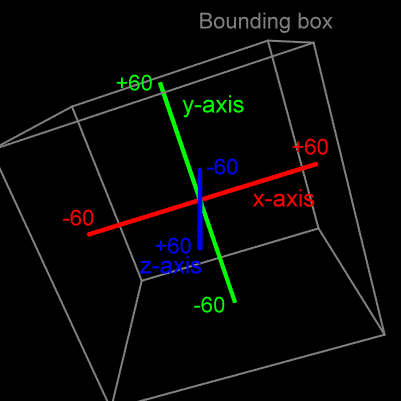
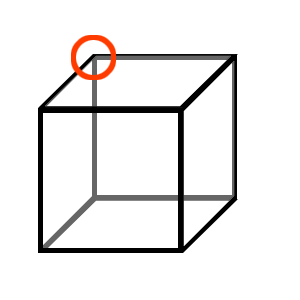
Positioning: Lets move it
Positioning from the center is not ideal,
so we moved the origin point of the models to be at
the top-left-back corner:
Lighting/Shadows
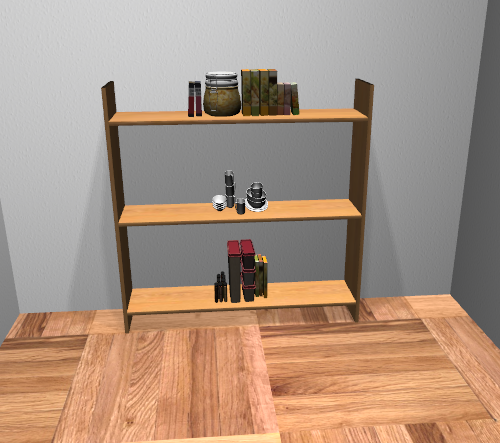

Lighting/Shadows
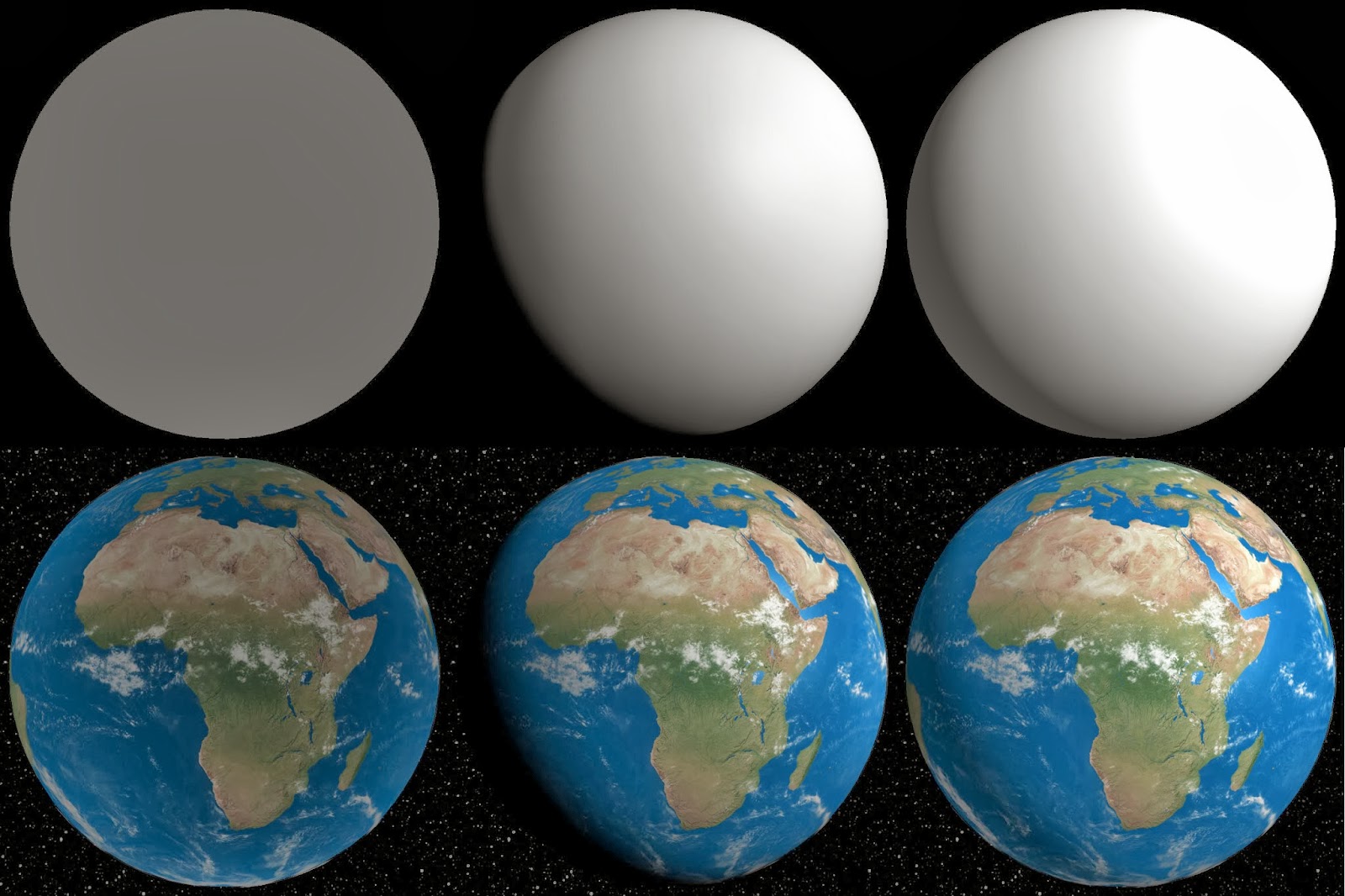

Types of lighting used: Ambient, directional, point.
Cutting/Resizing Products
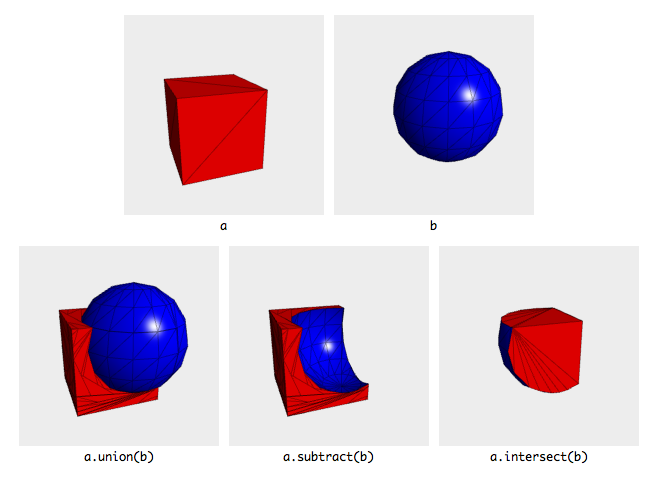
Doors
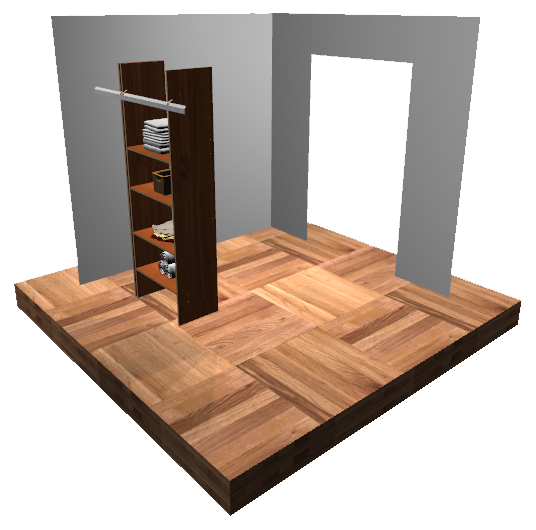

Camera Controls
Camera control types: Fly, orbit, path, pointer lock, trackball.
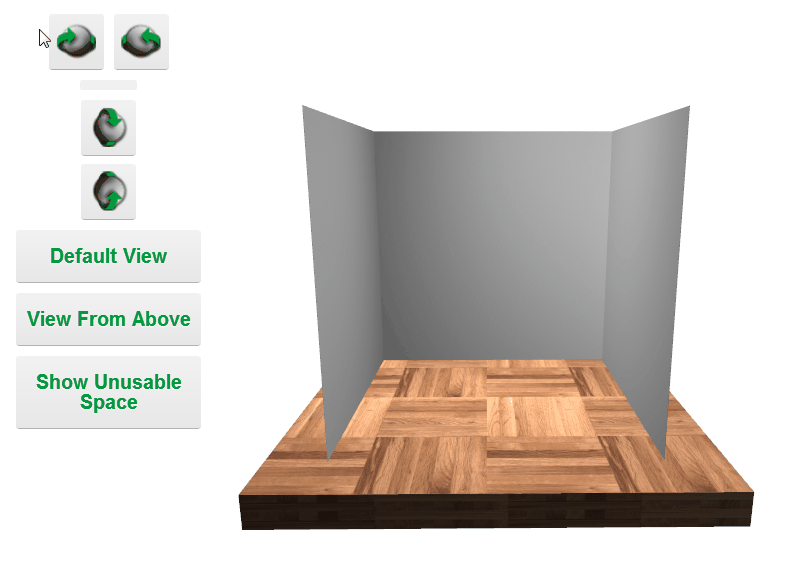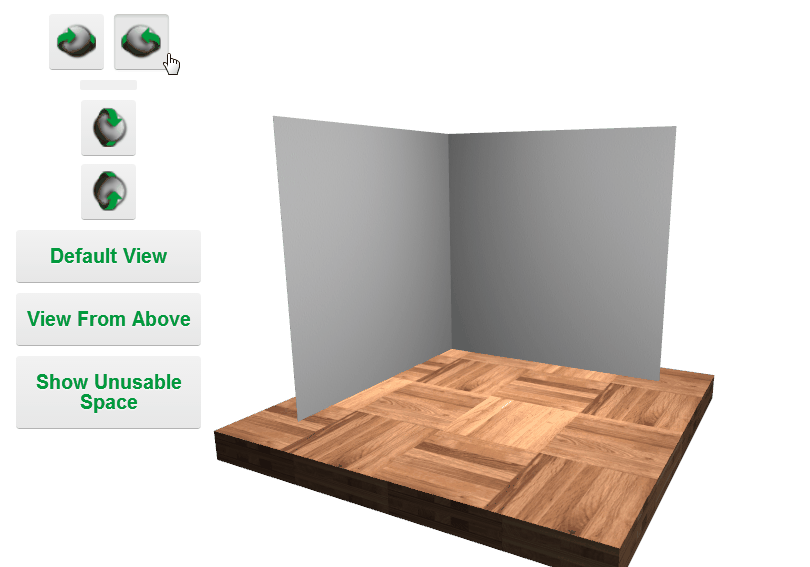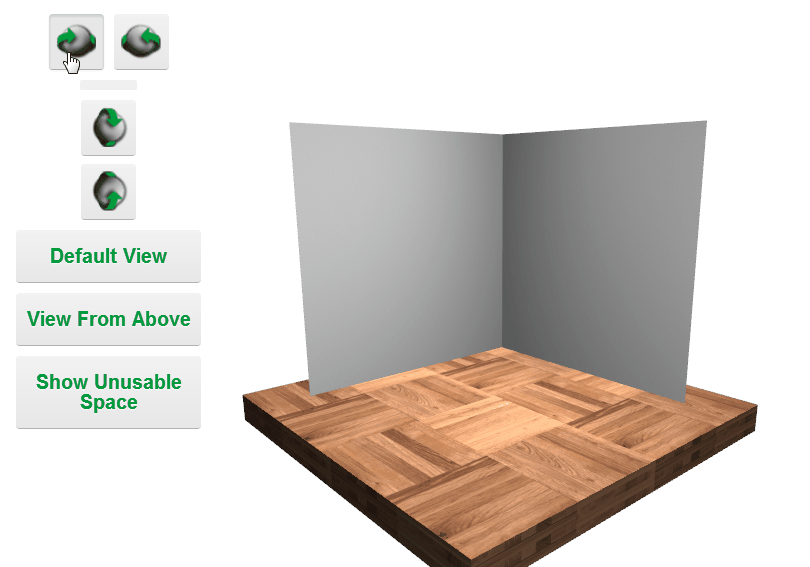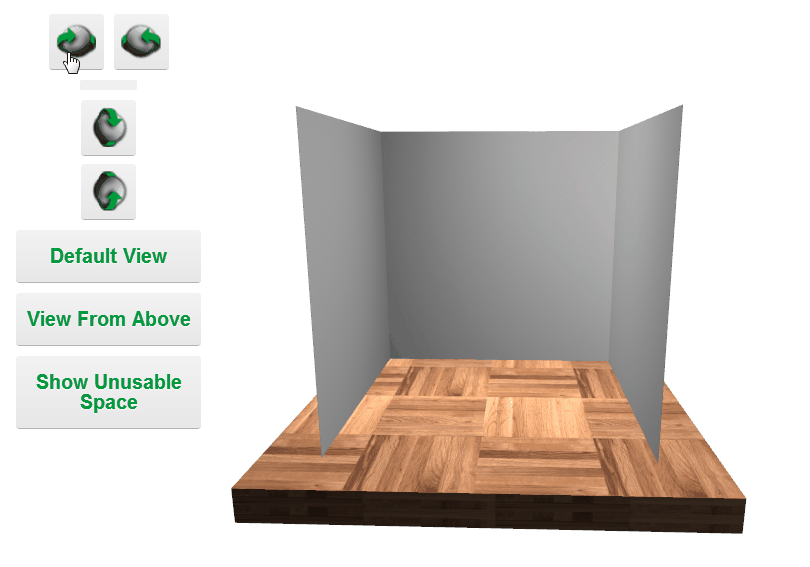
Minimizing File Size
Two methods used:
Remodeling
Destructive model reduction
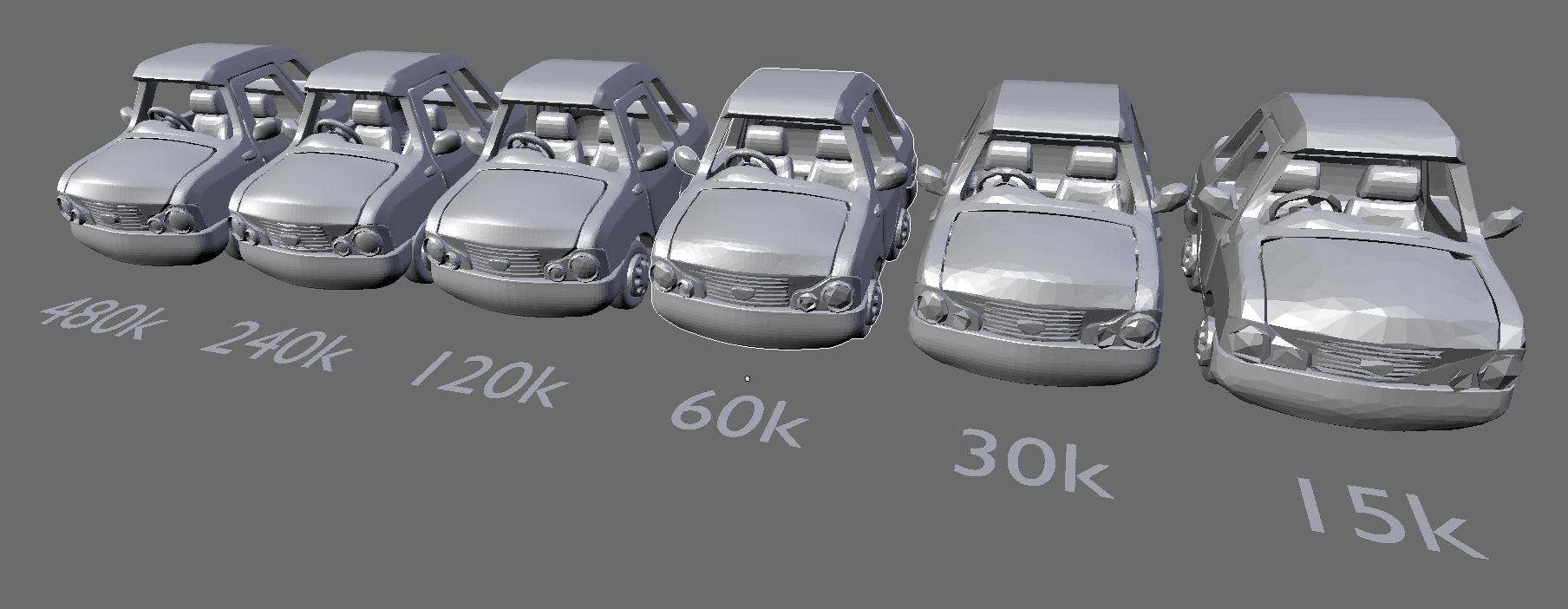

What did we Learn?
WebGL is hard
but
Three.js makes it a lot easier
Much less code to write
Don't have to write GLSL shaders (unless you want)
Lots of code examples and support
You can Do So Many Cool Things













Three.JS Is Always Improving
Over 7,000 commits, as of version 66
Migration Guides are provided for easier upgrading
Three.JS is more than just cool demos
Used in advertising:



Interactive Music Videos:


